Introduction
Alpha Centauri, the closest star system to our own, has long been a target for interstellar exploration. Recent advancements in technology and theoretical physics have made the prospect of reaching Alpha Centauri within a human lifetime more realistic than ever before. This article explores the technological breakthroughs and innovative concepts that could make this extraordinary journey possible.
The Significance of Alpha Centauri
Alpha Centauri is a triple star system located about 4.37 light-years from Earth. It includes three stars: Alpha Centauri A, Alpha Centauri B, and Proxima Centauri. Proxima Centauri, the closest of the three, has an exoplanet in its habitable zone, making it a prime candidate for the search for extraterrestrial life.
Proximity: At just over four light-years away, Alpha Centauri is the nearest star system to our own, making it an ideal target for interstellar missions.
Potential for Life: Proxima Centauri b, an exoplanet within the habitable zone of Proxima Centauri, could potentially support life, heightening interest in the system.
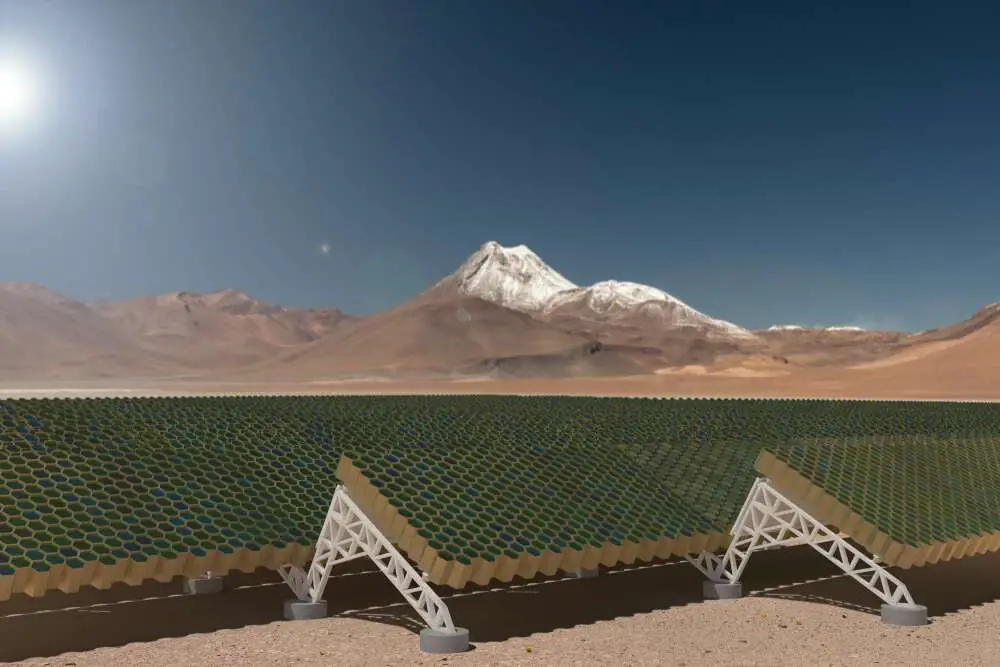

Breakthrough Starshot Initiative
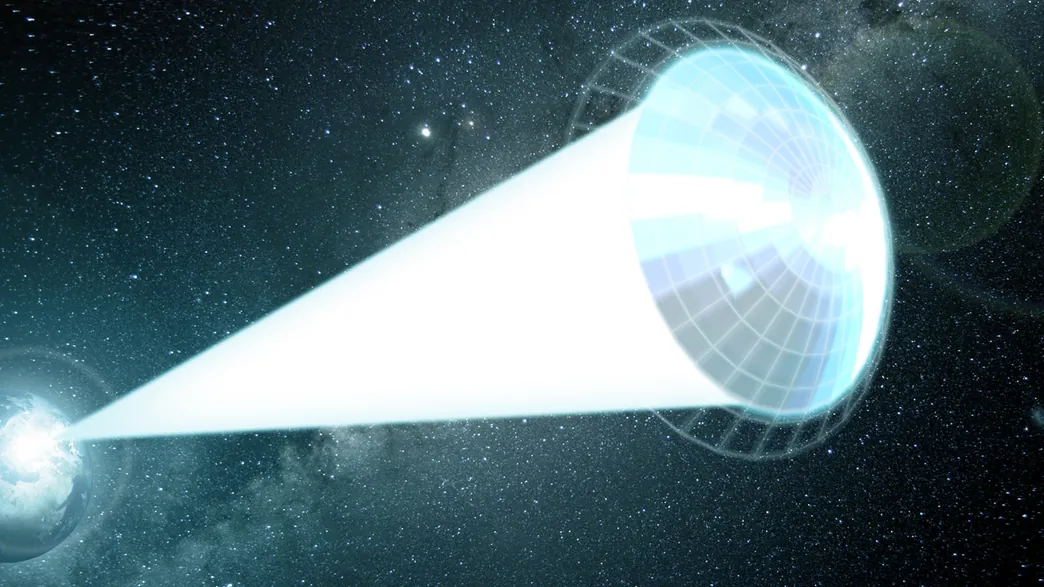
One of the most promising projects aimed at reaching Alpha Centauri is the Breakthrough Starshot initiative, announced in 2016 by physicist Stephen Hawking, investor Yuri Milner, and Facebook founder Mark Zuckerberg.
Nanocraft Technology: The initiative proposes sending thousands of tiny, lightweight nanocraft equipped with lightsails. These nanocraft would be propelled by powerful ground-based lasers, enabling them to travel at up to 20% of the speed of light.
Travel Time: At this speed, the nanocraft could reach Alpha Centauri in approximately 20 years, making it feasible to receive data within a human lifetime.
Advancements in Propulsion Systems
Recent developments in propulsion technology have also brought us closer to interstellar travel. Innovations such as antimatter propulsion, nuclear fusion drives, and the concept of a warp drive are all being explored.
Antimatter Propulsion: Utilizing antimatter as a fuel source could potentially provide the high energy density needed for interstellar travel, though the technology is still in its infancy.
Nuclear Fusion Drives: Fusion-powered spacecraft, like the proposed Direct Fusion Drive (DFD), could significantly reduce travel times to distant stars by providing a continuous and powerful thrust.
Warp Drive: Theoretical models based on Einstein’s general relativity suggest that a warp drive could create a “bubble” of spacetime, allowing faster-than-light travel without violating the laws of physics. Recent mathematical refinements have made this concept slightly more plausible.
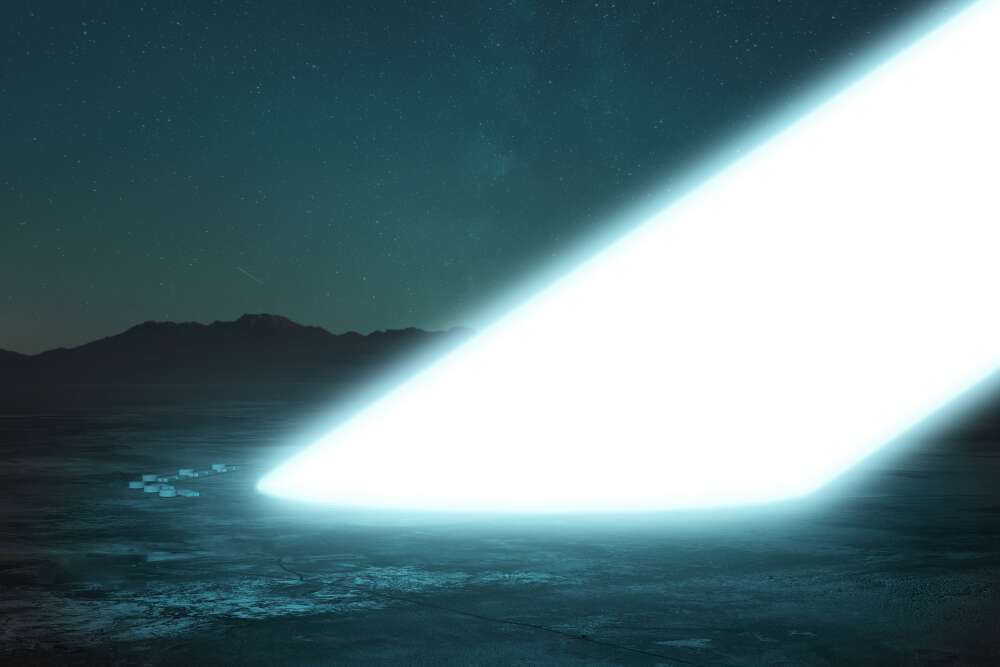

Challenges and Considerations
Despite the advancements, numerous challenges remain in making a mission to Alpha Centauri a reality.
Radiation Protection: Interstellar space is filled with high-energy cosmic rays and radiation. Protecting spacecraft and their payloads from this radiation is a significant engineering challenge.
Communication: Communicating with a spacecraft traveling at relativistic speeds over such vast distances presents unique challenges. Solutions need to be developed to maintain a reliable link with Earth.
Funding and Collaboration: Interstellar missions require substantial financial investment and international collaboration. Coordinating efforts and securing funding are crucial for the success of such ambitious projects.
Conclusion
The dream of traveling to Alpha Centauri within a human lifetime is inching closer to reality thanks to groundbreaking initiatives like Breakthrough Starshot and advancements in propulsion technology. While significant challenges remain, continued research and innovation hold the promise of making interstellar exploration a tangible goal for humanity.
For more detailed information, follow the latest updates on interstellar travel and related technologies in scientific publications and space exploration news.