
Introduction
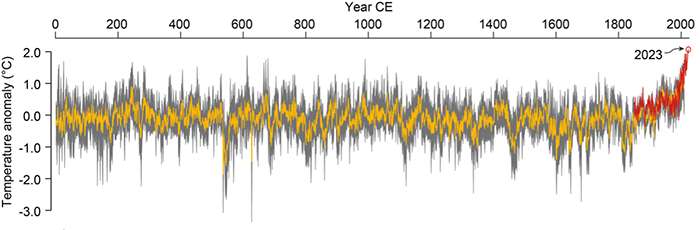
The summer of 2023 has officially gone down in history as the hottest in 2,000 years, according to recent climate studies. This alarming record is a stark reminder of the accelerating impacts of climate change and underscores the urgent need for comprehensive global action to address the escalating climate crisis.
Record-Breaking Temperatures
Unprecedented Heatwaves
Across the globe, 2023 witnessed unprecedented heatwaves that shattered previous temperature records. In many regions, temperatures soared to levels never before recorded, causing widespread disruptions and health crises. Europe, North America, Asia, and parts of Africa experienced prolonged periods of extreme heat, with some areas reporting temperatures exceeding 50 degrees Celsius (122 degrees Fahrenheit).
Scientific Analysis
A comprehensive analysis conducted by a team of climatologists and paleoclimatologists used a combination of modern temperature records, tree ring data, ice cores, and sediment layers to reconstruct historical climate conditions. Their findings revealed that the summer of 2023 was the hottest in two millennia, surpassing even the peak of the Medieval Warm Period (950-1250 AD) and the Roman Warm Period (250 BC-400 AD).
Impacts on Ecosystems and Society
Human Health
The extreme heat had profound impacts on human health, leading to a surge in heat-related illnesses and fatalities. Hospitals across many regions were overwhelmed with cases of heatstroke, dehydration, and other heat-related conditions. Vulnerable populations, including the elderly, children, and those with pre-existing health conditions, were particularly at risk.

Agricultural Disruption
Agriculture also faced severe challenges as crops wilted under the relentless heat. Drought conditions exacerbated by the high temperatures led to significant reductions in crop yields, threatening food security in many parts of the world. Farmers struggled to protect their livestock and maintain their livelihoods amid the extreme weather conditions.
Environmental Consequences
The natural environment did not escape unscathed. Forests and grasslands were scorched by wildfires, which became more frequent and intense due to the dry, hot conditions. Marine ecosystems suffered as well, with warmer ocean temperatures leading to widespread coral bleaching and the disruption of marine life patterns.
The Role of Climate Change
Anthropogenic Factors
Climate scientists emphasize that the record-breaking heat of 2023 is not an isolated event but a direct consequence of human-induced climate change. The burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial activities have significantly increased the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, leading to a steady rise in global temperatures.
Climate Models
Advanced climate models have consistently predicted an increase in the frequency and intensity of heatwaves as a result of global warming. The summer of 2023 serves as a stark validation of these models, highlighting the accuracy of climate science predictions and the urgency of implementing mitigation strategies.
Global Response and Future Actions
Policy Measures
In response to the extreme heat and its impacts, governments around the world have been prompted to take more aggressive action on climate change. Initiatives to reduce carbon emissions, transition to renewable energy sources, and enhance climate resilience have gained renewed urgency. The summer of 2023 has spurred new climate legislation and commitments to international agreements such as the Paris Accord.
Technological Innovations
Innovation and technology play crucial roles in addressing climate change. Advances in renewable energy technologies, carbon capture and storage, and sustainable agricultural practices are being accelerated to mitigate the impacts of climate change. Additionally, early warning systems and heat adaptation strategies are being developed to protect communities from future heatwaves.
Public Awareness and Advocacy
Public awareness and advocacy have also seen a surge as a result of the extreme heat. Grassroots movements, environmental organizations, and concerned citizens are increasingly vocal about the need for urgent climate action. Educational campaigns are raising awareness about the causes and consequences of climate change, encouraging individuals and communities to adopt more sustainable lifestyles.
Conclusion
The summer of 2023 stands as a sobering reminder of the realities of climate change. As the hottest summer in 2,000 years, it underscores the critical need for immediate and sustained action to mitigate the effects of global warming. The unprecedented heatwaves and their far-reaching impacts on health, agriculture, and the environment highlight the urgency of global cooperation and innovative solutions. Only through collective effort and commitment can we hope to safeguard our planet for future generations and prevent even more extreme climate events in the years to come.
