Introduction
In a groundbreaking discovery, NASA’s Mars rover has identified three potential signs of ancient life on a single rock. This finding has reignited hopes of uncovering past life on the Red Planet and offers new insights into Mars’ history and habitability. This article explores the details of the discovery, the significance of each sign, and the implications for future Mars exploration.
The Discovery
The Mars Rover Mission
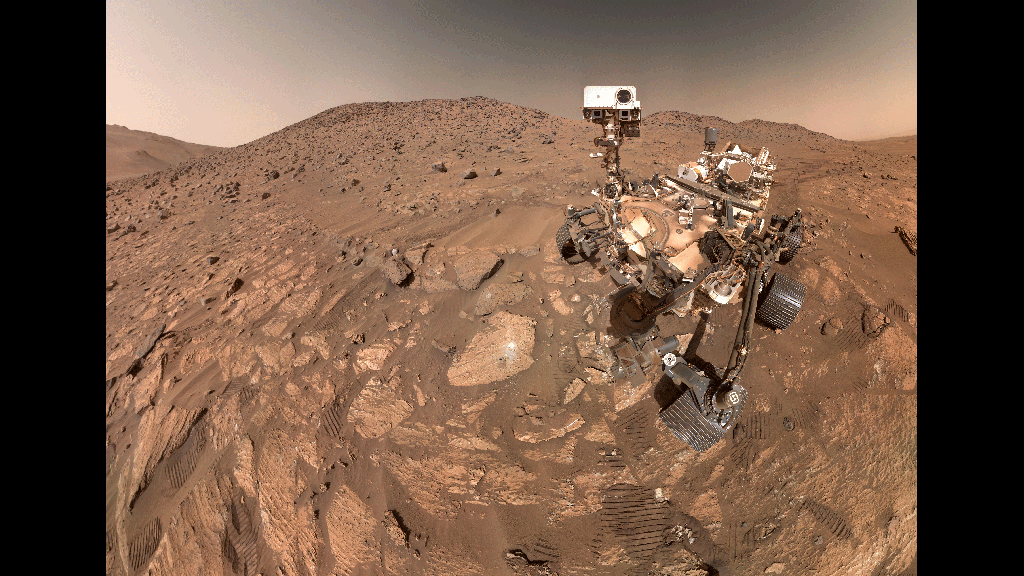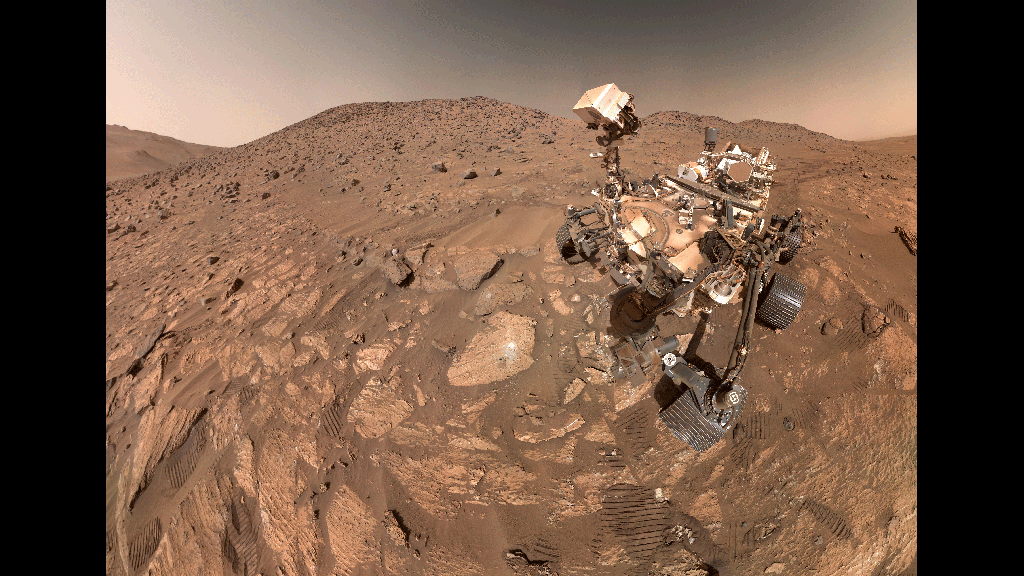
Rover Name and Launch: The Perseverance rover, launched in July 2020, has been exploring the Jezero Crater on Mars since February 2021.
Mission Goals: Perseverance aims to search for signs of ancient life, collect samples for future return to Earth, and study Mars’ geology and climate.
The Rock Sample
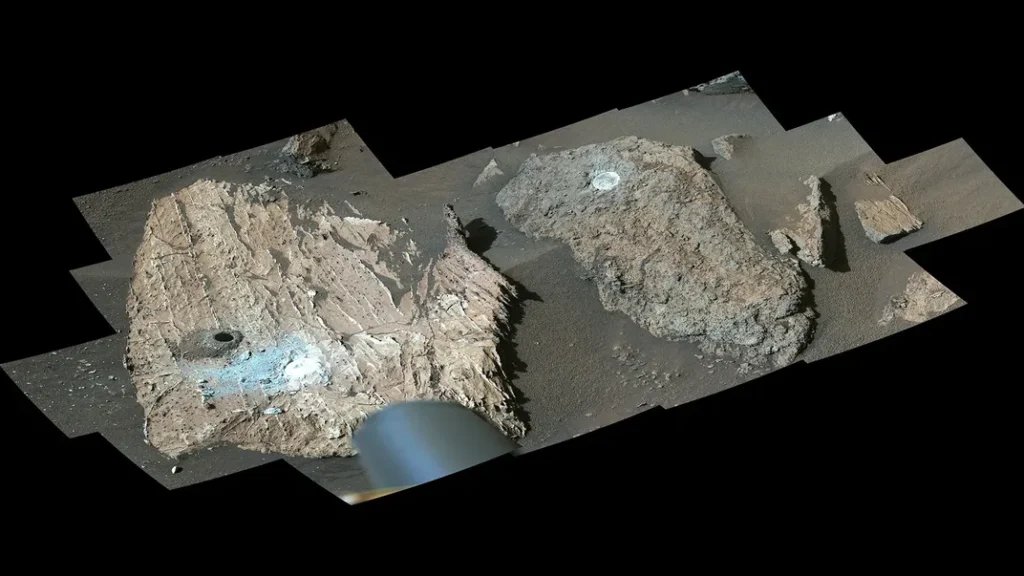
Location and Context: The rock, nicknamed “Enigma,” was found in the Jezero Crater, an area believed to have once hosted a lake and river delta.
Initial Observations: High-resolution images and data collected by the rover’s instruments revealed intriguing features on the rock’s surface.
Signs of Ancient Life
Organic Molecules
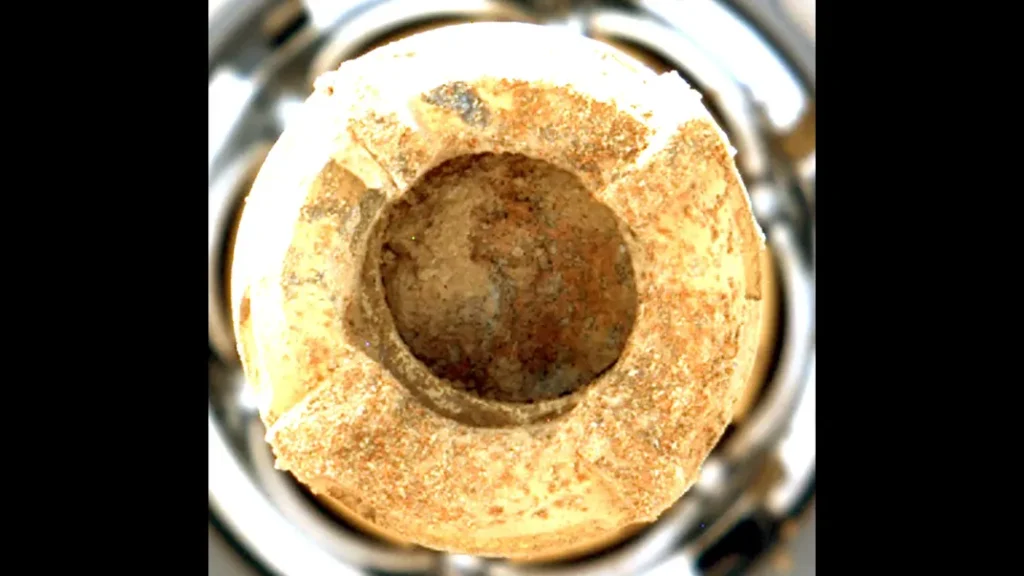
Detection Method: Using the SHERLOC (Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman & Luminescence for Organics & Chemicals) instrument, Perseverance detected complex organic molecules embedded in the rock.
Significance: Organic molecules are the building blocks of life, and their presence suggests that the rock may have been part of a habitable environment in Mars’ past.
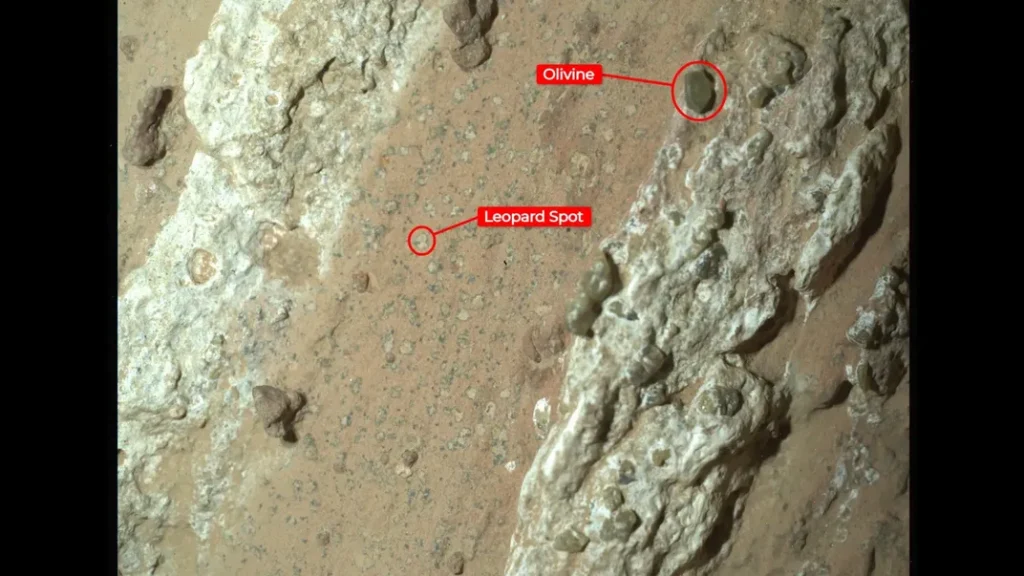
Microbial Mats
Visual Evidence: Close-up images of the rock surface show structures resembling microbial mats, which are layered biofilms created by colonies of microorganisms.
Implications: If confirmed, these structures could indicate that microbial life once thrived on Mars, leaving behind fossilized evidence of their presence.

Chemical Signatures
Spectral Analysis: Perseverance’s instruments identified specific chemical signatures within the rock that are typically associated with biological processes on Earth.
Potential Biogenic Origins: The presence of these chemical signatures could point to biological activity in Mars’ ancient past, supporting the hypothesis of past life.

Implications for Mars Exploration
Understanding Mars’ History
Past Habitability: The discovery of potential signs of ancient life provides strong evidence that Mars once had conditions suitable for life, including liquid water and a stable climate.
Geological Insights: Studying the rock and its features helps scientists understand the geological processes that shaped Mars’ surface and its potential to support life.

Future Missions and Research
Sample Return Mission: NASA and ESA (European Space Agency) are planning a Mars Sample Return mission to bring samples collected by Perseverance back to Earth for detailed analysis.
Continued Exploration: The findings will guide future missions to Mars, focusing on areas with high potential for discovering more signs of past life.
Broader Impact
Search for Life Beyond Earth: Discovering signs of ancient life on Mars would have profound implications for the search for life elsewhere in the solar system and beyond.
Astrobiology: The study of these potential biosignatures advances the field of astrobiology, providing new avenues for understanding life’s origins and evolution.
Conclusion
The identification of three possible signs of ancient life on a single rock by the Perseverance rover marks a significant milestone in Mars exploration. Organic molecules, structures resembling microbial mats, and specific chemical signatures all point to the possibility that Mars once hosted life. As scientists continue to analyze these findings and prepare for future missions, the dream of uncovering ancient life on Mars moves closer to reality, promising exciting discoveries and a deeper understanding of our place in the universe.